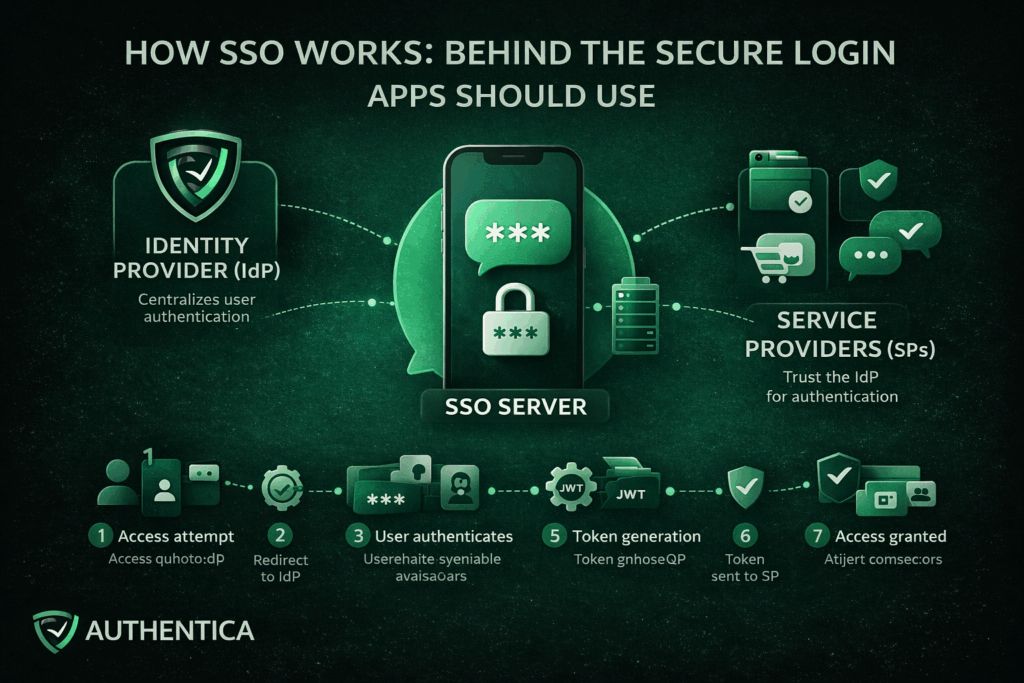
Single Sign-On (SSO) is an authentication method that allows a user to authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications or services with one account and without being required to log in again for each individual system.
Rather than each application independently managing usernames, passwords and authentication logic, SSO centralizes authentication in one account Once identity is verified, access is granted widely to multiple systems or apps, requiring just a single click for login.
Single Sign-On works by establishing a trusted connection between applications or services and a trusted Identity Provider (IdP). Instead of applications directly authenticating users, they delegate authentication to the IdP. When a user successfully proves their identity with a password or OTP or face recognition, the IdP generates a secure token to confirm this authentication for the platform and other connected ones.
This approach separates identity verification and security from the application. This means that they no longer need to store passwords or manage login, focusing on the quality of the delivered service.
Key Components of an SSO System
The SSO environment is composed of these components that together form the entire lifecycle:
Identity Provider (IdP)
The Identity Provider is the developer of the SSO solution, responsible for authenticating users. It verifies credentials, enforces authentication policies, and serves as the trusted party that applications rely on to authenticate users to their apps and platforms.
Service Providers (SPs)
Service Providers are the applications or services that users want to access, like the app or platform you provide. Rather than authenticating users directly, they trust the IdP and accept validated tokens from them as proof of authentication.
SSO Server
The SSO server works on the coordination and management of the authentication requests, token exchanges, and session continuity between the IdP and the service provider.
Authentication Protocols
Protocols such as SAML 2.0, OAuth 2.0, and OpenID Connect define how authentication data is structured, transferred and validated. These protocols ensure interoperability and secure communication across different systems.
User Directory
The user directory acts as a centralization point for storing records and access information. Common examples include Active Directory or LDAP-based directories.
Authentication Tokens
Tokens confirm a user’s authenticated state and are stored with high security and cryptographic encryption. Examples of tokens include SAML assertions and JSON Web Tokens (JWTs). They are time-limited and digitally signed to prevent tampering and malicious attacks.
The SSO process follows a predictable sequence of stages, that we explain here without much technical complications:
The process begins when a user navigates to an application that uses SSO. At this stage, the application checks whether the user already has an active and valid session or not.
If no valid session exists, the application redirects the user to the Identity Provider. This redirect includes an authentication request that defines the application requesting it and the exact context of the authentication.
The Identity Provider prompts the user to authenticate. This may involve entering username and password, using OTP authentication, or using an existing authenticated session if one already exists.
Once authentication succeeds, the IdP generates an authentication token. This token contains identity information and metadata confirming that the authentication has occurred. The token is also digitally signed using a trusted certificate.
The token is sent back to the original application, typically through a secure browser redirect or back-channel communication. This way, the application has received the token without directly handling user credentials.
The application validates the token by checking its signature, issuer, expiration time, and intended user. This ensures the token has not been altered and originates from a trusted source.
If the token is valid, the application establishes a session for the user and grants access. From this point forward, the user is considered authenticated with SSO.
A Readily Developed SSO Service from Authentica
For organizations looking to implement SSO without the complexity of building and maintaining their own infrastructure, Authentica offers a readily developed SSO service designed to integrate seamlessly with modern platforms and applications.
The service provides centralized authentication across cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid applications with one API, enabling organizations to unify access management with minimal effort and system disruption and with on-demand fee basis.
Single Sign-On is not just a user experience feature, but its true value lies in how it restructures authentication across systems. By understanding how it works, even with not every technical aspect, you have a better understanding of why SSO should be considered by every app or platform.

Online banking is fastly moving, and security remains one of the biggest considerations for competing companies in this space. One-time passwords (OTPs) remain one of the simplest, most effective ways to verify identity for banking and fintech applications. Their role has expanded significantly in the most recent years, especially in markets like Saudi Arabia, where digital banking adoption continues to grow rapidly.
If you are considering OTP for your banking operations or not sure about its value, we are sharing today what OTP is, why it matters, where banks use it and how they are delivered.
What Is OTP in Banking?
A one-time password (OTP) is a short verification code, typically 4 or 6 digits, that is generated automatically to authenticate a login or a transaction. Unlike static passwords, an OTP expires after one use or after a few minutes or seconds pass, reducing the risk associated with password reuse, credential leaks or unauthorized access.
An OTP essentially acts as a temporary PIN to improve security. Banks rely on it because:
Whether a user is logging in, transferring money or updating personal information, OTP ensures the request is from the owner of the account and not an intruder.
OTPs offer numerous benefits for banks and financial institutions of all types, helping secure accounts and transactions, and way more than this.
Enhanced Security
The most obvious benefit of OTPs is the improved level of security it adds. Passwords are vulnerable to phishing and breaches, and OTPs introduce a dynamic element to them to make accounts unbreachable even if passwords are stolen. Breaching OTPs will be a whole other layer of security and needs more advanced attacks.
Quick and Real-Time Verification
When supported by a reliable OTP delivery infrastructure, the authentication process adds only a few seconds to the user journey without slowing down operations, so it is very reliable and doesn’t affect customer experience.
User-Friendly Experience
It doesn't need learning to use OTP even for the first time. Users simply receive a code and enter it. This makes OTP a widely accessible way for authentication that adds no barriers for different types of users.
Fraud Reduction
Unauthorized transfers, hacked accounts, and identity theft cases can drop significantly when OTP is integrated as a mandatory step. Even if credentials are compromised, OTP prevents attackers from completing transactions or using the user account in any malicious way.
Banks apply OTPs across a long list of high-value or security-sensitive operations. Some of the most common include:
Login Verification
Most banks now apply two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA), instead of relying on one authentication method. OTPs are delivered via SMS, email or app push notifications to ensure only authorized users can access accounts and create new accounts.
Fund Transfers
Before confirming money movement, domestic or international, banks often require entering an OTP. This is because it is one of the safest methods to confirm transfers, preventing attackers from sending funds even if they gain access to the user account.
Online Payments
Debit and credit card transactions often make OTP confirmation required. Many banking apps also allow users to whitelist trusted platforms to reduce the number of OTP confirmations.
Account Information Changes
Modifying sensitive data such as a mobile number, password, or email address can require OTP verification to ensure such action is initiated by the real account holder.
Cardless ATM Withdrawals
Some banks now allow withdrawals using OTP instead of a physical card. The customer simply enters the OTP at the ATM machine to complete the process.
Authentica provides a readily developed authentication solution for banks, fintech companies, and finance enterprises with leading security. The API, which relies on an on-demand payment model, is built for fast integration into banking systems and supports high-volume transactions without delays. Contact us to learn more.
OTP remains one of the simplest and most dependable authentication methods that can be used in the finance and banking industry. As online transactions grow and fraud tactics also evolve, banks in Saudi Arabia and other countries continue to rely on OTP to secure logins, confirm transfers, and protect personal data.

Passwords have always been the pillar of online security for decades, but as the world and technology advance, their flaws become harder to ignore. With the number of online accounts and apps used by every single user growing, users are burdened with remembering countless passwords, while organizations struggle to manage security of millions of users that put their entire future on the verge. Passwordless authentication gives one of the best solutions to this.
In this blog, we explore what passwordless authentication is, how it works, its key benefits, and when it makes sense to adopt it in your organization.
Passwordless authentication is a security method that allows users to access systems and applications without entering a password. Instead of knowledge-based credentials such as PINs or passwords, it uses authentication factors that include things that a user has (like the phone) or something that is unique in them (like their fingerprint).
This covers biometrics like fingerprints or facial recognition or something they possess like a trusted device such as a smartphone or hardware key. These methods eliminate one of the weakest links in security, which is the password that can be forgotten or stolen itself.
Using passwordless authentication doesn’t always mean discarding traditional methods overnight. Many organizations use it alongside other verification steps as part of utilizing multi-factor authentication (MFA), which means using multiple factors for authentication at once.
Types of passwordless authentication can be divided into two main types:
While traditional authentication, which has been used for years, relies heavily on knowledge factors like passwords and PINs, passwordless authentication leverages possession and inherence factors to verify identity instead. This transformation removes the need for static credentials that can be stolen or reused.
The happens typically has three simple steps:
Registration: The user’s device or biometric data is securely registered with the system as they sign up.
Attempted Authentication: When logging in, the user confirms their identity through a fingerprint, facial scan or hardware key.
Verification: The system verifies the identity by matching the presented factor with the stored digital credential, granting access if it matches.
Unlike passwords, these credentials are never transmitted or stored in plain text, making them significantly harder for attackers to exploit.
Benefits of Passwordless Authentication
The move toward passwordless authentication is not only a security upgrade, as its usability and cost-efficiency are also outstanding. Organizations that adopt passwordless authentication methods can utilize benefits like:
Enhanced Security
This is clearly the main benefit and motive behind going to passwordless authentication. By removing passwords entirely, organizations reduce exposure to common cyber attacks like phishing, credential stuffing and old school brute-force attacks. Since there are no passwords to steal, attackers lose one of their most effective tools.
Better User Experience
If users no longer need to memorize or reset complex passwords, and can use a quick biometric scan or one-time code in a few seconds, that is definitely a great upgrade for usability. This enhanced usability can improve user satisfaction from apps and devices.
Reduced Operational Costs
Password management and storage is expensive and time-consuming. Large organizations spend millions each year handling password resets and managing security incidents. Passwordless systems drastically lower these costs by eliminating the need for customer support and reducing the risk of breaches.
Regulatory Compliance
Guidelines like GDPR, PCI-DSS and NIST emphasize strongly on authentication. Passwordless solutions often meet or exceed these requirements, helping organizations maintain compliance as they boost security and user experience.
One of the biggest draws of passwordless authentication methods like the biometric ones is the high initial costs and need of continuous development. Authentica resolves this with a readily developed solution with no need of initial investment as you pay as you go. Contact us to learn more about it.
Passwordless authentication isn’t a temporary trend for better usability or a trending feature added to apps, it’s a fundamental shift in how digital security is handled. It addresses the long-standing vulnerabilities of passwords while offering faster, safer and more user-friendly access. As cyber threats evolve, the elimination of passwords represent progress toward stronger digital protection and a smoother user experience.

Protecting identities, user and enterprise sensitive information is becoming more complicated than ever, especially with the ongoing AI boom. Traditional password-based verification methods, while more familiar and seem to be an easier option for many users, have been proven to be vulnerable to many attacks and errors.
Biometric authentication offers an alternative to passwords and more vulnerable authentication methods, as users verify identity through unique traits rather than something users have to remember or carry that can be stolen.
In this blog, we will explore what biometric authentication is, how it works, the main types of biometric authentication, and when to use them.
Biometric authentication is a security process that confirms a person’s identity by analyzing their unique biological traits like fingerprints, facial features or voice. These characteristics are captured and stored and compared to the user input each time they authenticate.
Unlike passwords or tokens that can be stolen or forgotten, biometric identification is unique to each person and nearly impossible to replicate accurately. This makes biometric authentication both highly secure and convenient and this is why it is now widely used in verifying online transactions, unlocking smartphones and even granting physical access to highly secured facilities.
Biometric authentication comes in many forms, each with its unique advantages and suitable applications. Understanding these types helps organizations choose the right mix of authentication methods to use, depending on their industry and user needs and preferences.
Fingerprint authentication analyzes the unique fingerprint patterns on a fingertip using optical, capacitive, or ultrasonic sensors. It is one of the most common and cost-effective biometric authentication methods, widely used in smartphones to authenticate apps and unlock the phone itself, in addition to access control and attendance management systems.
With facial recognition, the user face is mapped and key facial features are analyzed, such as the distance between eyes or the contour of the jawline, to create a mathematical representation of a face that is stored and later compared while logging in.
It offers quick, contactless verification and is commonly used for smartphone security, airport check-ins, and corporate access systems.
These methods analyze the unique patterns in a person’s eyes, more specifically the iris or the retina. Both are highly accurate and ideal for environments that demand top-level security, such as border control and government systems.
Voice authentication identifies a user by analyzing vocal characteristics such as pitch, tone and cadence. It’s particularly effective and widely used for phone banking, virtual assistants, and call center verification.
This category includes gait recognition (how a person walks), typing rhythm, and even mouse movement patterns in some advanced applications. It enables continuous authentication, monitoring users passively while they interact with systems to detect anomalies or unauthorized access.
Vein recognition is another biometric authentication method that uses infrared light to map the unique pattern of veins in a person’s hand or fingers. Similarly, hand geometry measures finger length and palm structure. Both methods are mostly suited to secure facility access and can be used in other healthcare applications.
Biometric authentication is increasingly adopted across industries because it provides a strong balance of security, efficiency and user convenience, which are the main factors that define which authentication methods are used to secure devices, facilities or user accounts. These are the biggest benefits of using biometric authentication instead of other traditional authentication methods:
Biometric traits are unique and difficult to counterfeit, making them highly resistant to attacks such as phishing or credential theft. The reliance on biological features rather than knowledge-based credentials significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, which is one of the biggest and most clear benefits.
With biometric authentication, users no longer need to remember or reset complex passwords every time they open one of their accounts. A fingerprint scan or facial recognition takes seconds, enabling fast authentication with unmatched convenience compared to any other type of authentication.
While initial setup costs for biometric authentication methods, especially advanced ones like face recognition, can be higher than traditional systems, biometric authentication reduces ongoing expenses tied to password management, recovery and the amount of support provided. Over time, this translates into substantial savings for organizations.
For industries governed by strict regulations, such as finance or healthcare, biometric authentication helps meet compliance standards like Know Your Customer (KYC), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), and different data protection laws by ensuring strong, verifiable identity checks that are in many cases obligatory.
Although biometric authentication can be applied broadly, its adoption can be more beneficial for specific industries, where it adds the most value. Here is where biometric authentication shines most:
Sectors such as defense and government benefit from the heightened security biometrics offer, minimizing risks associated with credential-based breaches that can’t be afforded.
Hospitals can use biometric authentication methods like fingerprint and iris recognition to ensure accurate patient identification and protect confidential health records.
Banks and fintech platforms adopt biometric authentication for seamless, secure verification in mobile banking, transaction confirmation and call centers.
Airports and immigration systems use facial recognition and iris scanning to speed up passenger processing while maintaining security integrity.
Mobile apps now use biometric authentication widely for unlocking apps, authorizing purchases and orders and protecting personal accounts.
Implementing biometric authentication from scratch can be complex, requiring deep expertise in security, user experience and system integration. Authentica simplifies all of this with a readily developed biometric authentication API, bringing facial recognition, fingerprint matching and voice verification. Developers can easily access this API on platforms like **[RapidAPI]**, and an **[n8n node]** is available for integration into automation workflows, without building them internally and wasting money and resources. You can get in touch with our team to learn more.
Biometric authentication represents a major step forward in the evolution of digital authentication for devices and accounts. It combines security, convenience and speed in a way that traditional methods cannot match. From securing financial transactions to enhancing healthcare systems and mobile experiences, biometrics are redefining online security, especially with the ability to integrate it widely with tools like Authentica.
The adoption of Face ID technology is rapidly increasing across businesses in Saudi Arabia. This is due to the enhanced security and accuracy it provides for securing accounts, transactions and devices, as well as its proven prevention of identity theft, making digital services more trustworthy.
Face ID also ensures seamless user experience, with enhanced ability of compliance and risk management, which allow companies to achieve operational efficiency, mitigate risks and cut down costs. If you are considering Face ID for your platform in Saudi Arabia or not sure about its value, we will dive into everything related to it in this blog.
Face ID refers to advanced facial recognition technology that verifies a person's identity using unique biological facial features. The primary objective of Face ID is to confirm that the user is truly who they claim to be, making fraud attempts extremely difficult compared to traditional security methods.
The Face ID process typically involves capturing a live image or short video, analyzing facial landmarks, and creating a secure mathematical template that is compared with the user input every time they log in. This information helps businesses prevent impersonation and in some cases detect suspicious activities instantly.
In Saudi Arabia, facial recognition for identity verification is increasingly becoming required and governed by regulatory authorities such as the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) and the Capital Market Authority (CMA). This is specifically important for remote onboarding and KYC compliance applications.
Financial institutions, fintech companies, trading platforms, and digital service providers operating in the Kingdom are required to adopt strong identity verification methods like facial recognition or face ID. Face ID has emerged as one of the most reliable solutions to meet both local regulatory requirements in Saudi Arabia and international anti-money laundering (AML) standards.
Prevention of Fraud and Account Theft
By implementing advanced Face ID with liveness detection, businesses can stop fraudsters from using photos, videos, deepfakes or masks to bypass verification in apps and devices. This helps prevent financial crimes such as identity fraud, account theft, and unauthorized transactions in fintech apps.
Enhancing Compliance
Robust facial recognition helps institutions comply with SAMA's KYC regulations and international AML guidelines. This contributes to protecting the financial transactions from being exploited for malicious purposes while meeting regulatory requirements that allow you to scale into new markets.
Protecting Users and Building Trust
Because face ID prevents account takeover, unauthorized transactions and identity theft. This gives customers confidence that their accounts and funds are genuinely secure, which can translate into trust and a stronger brand.
Maintaining Reputation
Companies that adopt high quality Face ID solutions in terms of security and speed demonstrate commitment to security and innovation. This contributes to strengthening their brand in increasingly competitive digital markets.
Live Capture and Liveness Detection
The system uses the device camera to capture a real-time image or video. It immediately checks for signs of life such as skin texture, light reflection, and micro-movements to ensure the person is physically present.
Biometric Analysis and Template Creation
Facial characteristics are measured and converted into an encrypted mathematical model. This template cannot be reversed into a real photo, ensuring privacy and security.
Secure Matching
The new captured image is compared to the stored one in less than a second with extremely high accuracy. This ensures fast verification without compromising security standards.
Anti-Spoofing Protection
Advanced systems block printed photos, screen replays, silicone masks, 3D masks and even deepfake videos. This provides powerful protection even against advanced fraud attempts.
Combating Identity Fraud in Real Time
Face ID with active and passive liveness detection stops fake account creation and unauthorized access before damage occurs. This allows platforms to identify and prevent fraud instantly.
Full Compliance with SAMA and CMA Regulations
For many businesses like banks and other finance businesses, remote customer onboarding using certified facial recognition is now an accepted method for meeting eKYC requirements. This helps businesses adhere to local and international regulations effectively.
Protecting Users and Their Funds
Verified identities mean criminals cannot easily withdraw money, trade illegally or exploit stolen credentials for malicious purposes. Face ID provides an additional layer of security that protects user accounts and funds with confirmation in every transaction.
Building Long-Term Trust
When users know their platform uses cutting-edge Face ID, they feel safer and more likely to engage. This contributes to enhancing customer loyalty and increasing platform sign up and usage.
To complete the Face ID implementation successfully, businesses can utilize readily developed face ID APIs that cut down effort and cost, while delivering a high level of security like Authentica. When choosing the right tool, you need to consider these factors:
All of these qualities are provided by Auithentica. If you need to learn more, you can get in touch with our experts for a free consultation.
Face ID or face recognition plays a vital role in ensuring the security of digital transactions, accounts and devices. In Saudi Arabia, Face ID technology is governed by regulatory authorities, primarily the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) and the Capital Market Authority (CMA), which means it can be obligatory in many cases.

Facial recognition is one of the biometric authentication forms that has changed cybersecurity and expanded hugely to users in the past years. Consumers now access online accounts, apps, or devices by scanning their faces easily and seamlessly. This cuts down wasted time in logging in and signing up while keeping security strong.
Face recognition is also widely spreading and wanted by users. A poll by the finance giant VISA found that over 86% of people prefer biometrics like facial recognition and voice recognition over passwords for identity checks or payments. Moreover, more than 131 million Americans use it daily for apps, accounts, or devices.
In this article, we cover face recognition technology for identity verification for all types of purposes including two factor authentication, how it works for verification, its benefits, comparisons to other methods and how to offer it to your users with no development.
Face recognition system verifies or identifies people using unique facial features, letting them access accounts and devices. During the authentication process, which can be two factor authentication for account protection, the system captures a new image of the user and compares it to the stored template. A successful match grants access or confirms identity, making the process both quick and precise.
Accuracy of face recognition in modern systems has improved dramatically, with top algorithms reaching over 99.5% reliability. This level of precision allows advanced systems to even distinguish between identical twins, something previously thought to be almost impossible.
Face recognition systems use cameras to capture images in either 2D or 3D, depending on the setup. They compare real-time data from photos or videos against stored records. Most implementations require internet connectivity since large databases are hosted on secure servers. The process involves advanced mathematical analysis, ensuring biometric matches without human error, and enabling seamless access to apps, services, systems, or even physical buildings.
The workflow of a face recognition feature typically consists of three main stages:
Facial recognition verifies identities with far greater accuracy than traditional credentials, considering the uniqueness of each human’s face characteristics. Unlike passwords or PINs that can be guessed, forgotten, or stolen, facial features remain unique and extremely hard to replicate.
Convenience is another key advantage. Users can unlock devices, authorize payments, or gain access to secure areas without needing to type passwords or carry physical keys. Once people experience the ease of using their face as a key, going back to older methods feels outdated and slow.
Compared to other biometric authentication ways, contactless operation adds a layer of hygiene and safety. Since there’s no need to touch fingerprint scanners, keypads, or doors, the spread of germs is minimized, something that proved especially valuable during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Facial recognition, when used for two factor authentication, instead of verifying identity of users (like in KYC for banking apps) takes a different approach compared to other two factor authentication methods like passwords, email verification, selfies, or even fingerprint scanning. This is how it briefly compares to each:
Businesses no longer need to build their own biometric systems from the ground up. Services like Authentica offer zero-coding biometric authentication, with the highest security standards and a pay-as-you-go model that minimizes initial costs.
Facial recognition is growing rapidly due to its security, convenience and speed. It is no doubt the best technology for identity verification, and for two factor authentication, it offers a very competitive choice in terms of security and convenience. One of its biggest downsides is that it needs complicated development, which can be resolved with a readily developed face recognition API as a service with no initial costs.

Two-factor authentication (2FA) has become essential for digital security, as it offers a robust way to protect user accounts from unauthorized access. For developers building applications, integrating 2FA is no longer optional. It's a necessity to ensure user trust and data safety. In this article, we’ll break down what 2FA is, explore its different types, guide you on choosing the right options for your app, and discuss the benefits of using a third-party vendor like Authentica.
Two-factor authentication is a security mechanism that requires users to verify their identity using two different ways before accessing an application or a platform. Unlike relying only on a username and password, 2FA combines something the user knows (like a password) with something they have (like a phone or a fingerprint).
This dual-layer approach significantly reduces the risk of account compromise, even if a password is stolen. By adding this extra step, 2FA makes it much harder for cybercriminals or people with malicious intents to hijack accounts through phishing or brute-force attacks.
There are several 2FA methods, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Below, we outline the most common options to help you understand their practical applications.
One of the most widely used 2FA methods involves sending a one-time code to a user’s phone or email. This code is called one time code or one time password (OTP). The user enters this unique code to verify their identity. SMS is the most popular delivery method, but voice calls or email are also widely used.
Pros: Relatively easy to implement and widely accessible, as most users already have a phone or email account.
Cons: SMS and voice calls are vulnerable to SIM-swapping or interception, and email-based codes offer limited security if the email account uses the same password as the primary account. Losing access to a phone number can also lock users out.
Push notifications send a login approval request to a user’s trusted device through a notification from an app, allowing them to approve or deny access by clicking the notification.
Pros: User-friendly and fast, requiring no code entry. Reduces phishing risks compared to SMS.
Cons: Requires an app on the user device. Can be vulnerable to accidental approvals if users aren’t cautious.
Apps like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator generate codes that are valid for a few seconds on the app on a user’s device, eliminating the need for network-based delivery. These codes vary by platform, so every service has its forever-changing unique code that changes every few seconds.
Pros: More secure than SMS, as codes are generated offline and harder to intercept. Works without mobile network access.
Cons: Requires users to install and manage an app, and losing the device can lead to lockout if not backed up properly.
Biometric methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, use a user’s face or fingerprint scan to get them through their accounts.
Pros: Extremely convenient, requiring no manual input.
Cons: Biometric data is sensitive and unchangeable, raising privacy concerns.
Location-Based Authentication
Location-based authentication usually serves as an implicit authentication factor, and is often used by services to flag logins from unexpected places.
Pros: Runs in the background, requiring no user action unless a login attempt is flagged.
Cons: Not highly reliable on its own, as IP-based location can be manipulated, and multiple users may share the same location.
Hardware keys, like YubiKey or Google Titan, use cryptography to authenticate both the user and the service, protecting against man-in-the-middle attacks.
Pros: A very secure 2FA method, resistant to phishing and interception. Simple to use, with just plug in or tap via NFC.
Cons: Expensive to distribute at scale, and keys can be lost or damaged.
Some services, like in Google accounts, provide users with a list of pre-generated one-time codes for authentication or transaction verification.
Pros: Highly secure due to their randomness and rarity of transmission, making interception difficult.
Cons: Storage is a challenge, as codes must be kept in a secure location,
Password as a Second Factor
In some cases, a password serves as the second factor. This is often seen in messaging apps like WhatsApp or Telegram. Here, a one-time SMS code acts as the first factor, and an optional password provides additional security.
Pros: Protects against loss of phone number access.
Cons: Relies on users setting strong, unique passwords, which isn’t always guaranteed.
Selecting the right 2FA methods for your application depends on your user base, security requirements, and any operational constraints. Here are key factors to consider:
Implementing 2FA from scratch can be complex, requiring expertise in cryptography, user management, and compliance. This is where third-party vendors like Authentica come in, especially with its Saudi market focus and expertise. Authentica provides pre-built 2FA solutions that integrate seamlessly with your application, saving time and reducing errors, so that you can focus on your app’s core functionality while outsourcing the complexity of secure authentication.
Two-factor authentication is a critical tool for safeguarding user accounts in an increasingly threat-filled landscape. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each 2FA method, whether it’s SMS, authenticator apps, biometrics, or hardware keys, you can make informed decisions about what to offer in your platform. Balancing security, usability, and cost is key, and using a trusted service like Authentica can simplify the process while ensuring robust protection.

In our rapidly evolving digital world, cybersecurity has become a top priority for individuals and businesses alike. With increasing threats and breaches, traditional passwords are no longer sufficient to provide the necessary protection. This is where the One-Time Password (OTP) comes in—a simple yet highly effective security technology that has revolutionized how we secure our accounts and digital transactions.
A One-Time Password (OTP), also known as a One-Time PIN, One-Time Authorization Code, or dynamic password, is an automatically generated alphanumeric code valid for a single login session or transaction [1]. Unlike static passwords that can be reused repeatedly, an OTP loses its validity immediately after use or after a very short period, making it a strong shield against many cyberattacks.
Imagine you are trying to log in to your online banking account. After entering your username and static password, the system asks you to enter an additional code sent to your mobile phone or email. This code is the OTP. Even if an attacker manages to steal your username and password, they will not be able to access your account without the unique OTP generated at that specific moment.
The mechanism of OTP relies on a simple yet powerful principle: generating a unique code for each verification process. When a user requests an OTP, the system generates this code using complex algorithms and then sends it to a trusted communication channel owned by the user, such as their mobile phone via SMS or WhatsApp, or their email. Once the user receives the code, they enter it into the system to complete the verification process.
There are two main types of OTPs:
1.Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP): These codes are valid for a very short period, usually 30 or 60 seconds. They are generated using an algorithm that combines a shared secret key and the current time. This is the most common type used by authentication apps like Google Authenticator.
2.HMAC-based One-Time Password (HOTP): These codes rely on a counter that increments with each use. The code is generated using a shared secret key and the counter value. Each time a code is used, the counter increases, ensuring that the next code will be different. This type is less common in daily use but equally effective.
Several reasons make OTP a fundamental component of modern security strategies:
•Protection Against Password Theft: Even if attackers manage to obtain your static password through phishing, malware, or data breaches, they will not be able to access your account without the real-time generated OTP.
•Combating Replay Attacks: Since each OTP is valid only once, attackers cannot intercept the code and reuse it later for unauthorized access.
•Enhancing Trust and Security: OTP provides an additional layer of security, reassuring users that their accounts and transactions are well-protected. This builds trust in digital services and increases adoption rates.
•Compliance with Regulatory Standards: Many industries, such as financial services and healthcare, require high levels of security and identity verification. OTP helps companies comply with these regulations and standards.
•Ease of Use: Despite its technical complexity, OTP is easy for the end-user to use. All it requires is entering a code consisting of a few digits or characters, which is a quick and intuitive process.
Authentica understands the importance of providing robust and flexible verification solutions to meet diverse business needs. For this reason, Authentica offers a comprehensive suite of multi-channel OTP solutions, ensuring that businesses can secure their operations and authenticate their users with confidence and ease. Authentica is a product of T2, a leading company in providing innovative technical solutions.
Short Message Service (SMS) is one of the most common and reliable methods for sending OTP codes. This method is widely adopted, as most people own mobile phones and can easily receive text messages. Authentica offers an SMS OTP solution that ensures fast, secure, and highly reliable delivery of codes. Whether you need two-factor authentication (2FA), phone number verification during registration, or account recovery, Authentica's SMS OTP provides the ideal solution. The solution boasts industry-leading delivery rates (99.9%+) and transfer times faster than a second, supported by a redundant global infrastructure. It also allows you to use your own sender ID and branded templates to enhance trust and provide a professional experience.
With the growing popularity of WhatsApp as a primary communication platform, sending OTP codes via WhatsApp has become an attractive option for many businesses. Authentica's WhatsApp OTP provides a secure and familiar way for users to receive verification codes. Codes are sent directly via WhatsApp using an officially approved sender name, which enhances your brand identity and gives the user a smooth and reliable experience. This solution features seamless integration, secure messaging with end-to-end encryption, and the use of a familiar channel that users already trust. This solution is ideal for businesses that want to reach their customers through their preferred channels.
Despite the emergence of new channels, email remains an effective and reliable method for sending OTP codes, especially in cases such as account registration, password recovery, and sensitive operations. Authentica's Email OTP provides a reliable and flexible solution for sending verification codes to user emails with messages that carry your brand identity. This solution features professional, customizable email templates, sending using a trusted sender domain, local and international delivery support, and accurate reports to track delivery and open rates. Authentica's Email OTP ensures fast delivery consistent with your brand identity, enhancing the verification experience and providing professionalism without complexity.
•Multi-Channel Verification from One Place: Authentica provides a unified platform for user verification via SMS, WhatsApp, and email, in addition to extra tools like biometric verification .
•Tailored Solutions for Every Sector: Whether you operate in financial and tech services, e-commerce, health and education, or government and law, Authentica offers customized solutions that precisely meet your sector's needs.
•Easy Integration for Developers: Authentica's solution features quick technical integration via clear API interfaces, making it suitable for startup teams and large organizations.
•Real-time Visibility and Full Control: You can monitor every verification attempt in real-time, with tracking of sending and response status, and built-in alternative options.
•Scalability with High Security: From hundreds to millions of users, Authentica ensures performance and compatibility at every level, while maintaining the highest security standards.
To further streamline integration and workflow automation, Authentica provides its own plugin for the popular automation platform N8N. This integration allows developers and businesses to easily connect Authentica's services with hundreds of other applications and services, opening new possibilities for seamless automation and verification. You can find Authentica's N8N plugin
In an era of increasing cyber threats, One-Time Passwords (OTP) have become an indispensable tool for enhancing digital security. By providing an additional layer of protection, OTP helps individuals and businesses protect their accounts and transactions from unauthorized access. Authentica, as a product of T2, offers multi-channel OTP solutions (SMS OTP, WhatsApp OTP, Email OTP) that combine strong security with flexibility and ease of use, making it the ideal partner for any company seeking to enhance its digital security and customer trust.

In the bustling world of e-commerce, where transactions happen at the speed of light, the threat of fraud looms large. As online shopping continues its meteoric rise, so too does the sophistication of those looking to exploit digital vulnerabilities. For every innovative e-commerce platform, there's a determined fraudster seeking to undermine its security. But what if your strongest defense wasn't a complex web of algorithms, but a simple, yet powerful, concept: robust authentication?
This post will dive into the critical role of identity verification in safeguarding your online business. We'll explore the evolving landscape of e-commerce fraud, highlight the fundamental principles of authentication, and demonstrate how a comprehensive authentication strategy can transform your digital storefront into a fortress against financial crime. Get ready to discover how prioritizing secure user access can not only protect your bottom line but also build unwavering customer trust.
The digital marketplace, for all its convenience, presents a unique set of challenges. The absence of physical interaction means that verifying identities and intentions becomes paramount. Fraudsters exploit this distance, employing various tactics to siphon off profits and damage reputations. Understanding these threats is the first step in building an impenetrable defense.
E-commerce fraud isn't a single entity; it's a hydra with many heads, each requiring a specific countermeasure. Here are some of the most common forms:
•Account Takeover (ATO): Imagine a thief slipping into your customer's digital shoes. That's ATO. Fraudsters gain unauthorized access to legitimate customer accounts, often through stolen credentials from data breaches or phishing scams. Once inside, they can wreak havoc: making unauthorized purchases, draining loyalty points, or even altering personal information for future exploits. ATO attacks are particularly insidious because they leverage the very trust you've built with your customers.
•Card-Not-Present (CNP) Fraud: This is the digital equivalent of using a stolen credit card without the physical card. It's rampant in online transactions where the card isn't physically presented. Fraudsters use stolen card numbers, often acquired through various illicit means, to make unauthorized purchases. Detecting CNP fraud is a constant battle, as merchants lack the traditional verification methods available in brick-and-mortar stores.
•Friendly Fraud (Chargeback Abuse): This one stings because it comes from within. Friendly fraud occurs when a customer makes a legitimate purchase but then disputes the charge with their bank, claiming it was unauthorized or that they never received the goods. While some chargebacks are valid, many are a deliberate misuse of the system, costing businesses significant revenue in lost goods, shipping, and chargeback fees.
•Identity Theft and Synthetic Identity Fraud: This involves fraudsters using stolen personal information to create new accounts or make purchases. A more sophisticated variant, synthetic identity fraud, involves combining real and fabricated data to create entirely new, fictitious identities that can bypass basic verification checks. These fabricated identities are then used for a range of financial crimes.
•Return and Refund Fraud: This category includes customers falsely claiming non-receipt of items or returning stolen or damaged goods to obtain refunds or exchanges, directly impacting a retailer's inventory and profitability.
These threats underscore a crucial point: in the digital age, proactive and intelligent fraud prevention isn't just an option; it's a necessity. It's about safeguarding your assets, preserving your reputation, and ensuring a secure, seamless experience for your genuine customers.
Think of authentication as the digital bouncer at the door of your e-commerce store. Its job is simple: verify that everyone entering is who they say they are. In the online world, where physical presence is absent, this verification becomes the bedrock of security. A robust authentication system is your primary defense, ensuring that only legitimate customers can access their accounts, make purchases, and interact with your platform.
Authentication relies on proving identity through various factors. These are often categorized as:
•Something You Know: This is the most familiar – passwords, PINs, or secret questions. While common, they are also the most vulnerable to theft or guessing.
•Something You Have: This involves a physical item in your possession, like a mobile phone receiving a one-time code, a security token, or a smart card. The idea is that only the legitimate user would have access to this item.
•Something You Are: This is where biometrics come into play – unique biological traits like fingerprints, facial features, or even voice patterns. These are generally considered the most secure as they are incredibly difficult to replicate.
Authentication methods have evolved dramatically as cyber threats have grown more sophisticated:
•Single-Factor Authentication (SFA): The old guard, typically just a password. Easy to use, but a single point of failure that fraudsters love to exploit.
•Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): The modern standard. MFA requires two or more different types of verification before granting access. This could be a password combined with a code sent to your phone. It’s a significant leap in security, making it exponentially harder for unauthorized users to break in.
•Passwordless Authentication: The future is here, and it doesn't involve remembering complex character strings. Passwordless methods eliminate traditional passwords, relying instead on more secure and user-friendly alternatives like biometrics or magic links. This not only boosts security by removing the most common attack vector but also streamlines the user experience.
For any online business, strong authentication isn't just a technical feature; it's a strategic imperative. It directly impacts your security, your reputation, and your bottom line:
•Fortifying Against Account Takeover: By demanding more than just a password, strong authentication makes it incredibly difficult for fraudsters to hijack customer accounts, even if they've managed to steal credentials.
•Securing Every Transaction: During checkout, robust authentication verifies the cardholder's identity, significantly reducing the risk of fraudulent purchases and costly chargebacks.
•Building Unshakeable Customer Trust: When customers feel their data and transactions are secure, their confidence in your brand soars. This translates to increased loyalty and repeat business.
•Streamlining Compliance: Many global regulations now mandate strong customer authentication for online payments. Implementing these measures ensures you meet legal requirements and avoid penalties.
In essence, strong authentication is the invisible shield protecting your e-commerce ecosystem. It's the assurance that every interaction on your platform is legitimate, secure, and trustworthy.
At Authentica, we understand the unique security challenges faced by e-commerce businesses. We provide a comprehensive suite of authentication solutions designed to be both powerful and user-friendly, ensuring your digital storefront is protected without compromising the customer experience. Our focus is on delivering flexible, fast, and reliable identity verification that integrates seamlessly into your existing systems.
Here are some of the key authentication types we offer, each designed to provide a robust layer of security:
•SMS OTP: A simple yet effective way to verify user identity by sending a one-time password via text message to their registered mobile phone. Learn more about our SMS OTP solution.
•WhatsApp OTP: Leveraging the popular messaging platform, we enable secure OTP delivery directly to your customers' WhatsApp, offering convenience and reliability. Discover our WhatsApp OTP solution.
•Email OTP: For those who prefer email-based verification, our Email OTP service provides a secure one-time password delivered to the user's registered email address. Explore our Email OTP solution.
•Face Recognition: Offering a frictionless and highly secure biometric authentication method, face recognition allows users to verify their identity with a glance. See how our Face Recognition works.
•Voice Verification: Utilize the unique characteristics of a user's voice for secure and convenient authentication, adding another layer of biometric security. Learn about our Voice Verification solution.
By integrating these multi-channel and advanced authentication methods, Authentica empowers e-commerce businesses to:
•Drastically Reduce Account Takeover (ATO): Even if credentials are stolen, the additional factor of an OTP or biometric scan makes it nearly impossible for unauthorized users to gain access.
•Minimize Card-Not-Present (CNP) Fraud: By requiring an extra verification step during checkout, we help confirm the legitimate cardholder, significantly cutting down on fraudulent transactions.
•Enhance Overall Security Posture: Our solutions provide a robust defense against various forms of fraud, protecting your business from financial losses and reputational damage.
•Improve User Experience: While adding security, our methods are designed for ease of use, ensuring a smooth and positive customer journey.
Ready to elevate your e-commerce security? Sign up today and experience the difference a comprehensive authentication strategy can make.

The challenge facing modern fintech companies in Saudi Arabia extends far beyond simple user verification. Traditional Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, while necessary for regulatory compliance, have become significant barriers to user adoption and business growth. The conventional approach requires multiple document uploads, manual verification steps, and lengthy waiting periods that can extend customer onboarding from minutes to days or even weeks.
Our case study focuses on a leading Saudi fintech company that recognized the urgent need to transform their customer onboarding process without compromising security or regulatory compliance. The company, which provides digital payment solutions and financial services to both consumers and businesses, was experiencing significant customer drop-off during the registration process. Initial analysis revealed that over 60% of potential customers abandoned their registration attempts before completion, primarily due to the complexity and time requirements of the traditional KYC process.
The existing onboarding process required customers to provide multiple forms of identification, including national ID cards, bank statements, and proof of address documents. Each document required manual review by compliance officers, creating bottlenecks that could delay account activation for several business days. The process was particularly challenging for younger users and those in remote areas who expected immediate digital experiences similar to those provided by global technology platforms.
The solution implemented by this forward-thinking fintech company centered on intelligent authentication that leveraged multiple verification methods while maintaining the highest security standards. The new system integrated seamlessly with Saudi Arabia's National Digital Identity platform (Nafath), enabling instant identity verification for Saudi nationals. This integration alone eliminated the need for manual document review in over 80% of cases, dramatically reducing processing time and improving user experience.
The intelligent authentication system employed risk-based assessment algorithms that could evaluate user behavior, device characteristics, and transaction patterns in real-time. Low-risk users with strong digital identity verification could complete onboarding in under three minutes, while higher-risk cases were automatically flagged for additional verification steps. This approach ensured that security standards were maintained while providing a smooth experience for the majority of legitimate users.
Biometric verification played a crucial role in the new onboarding process. The system utilized facial recognition technology to match users with their official identification documents, providing an additional layer of security while maintaining user convenience. The biometric verification process was designed to work seamlessly across different device types and lighting conditions, ensuring accessibility for all users regardless of their technical setup.
Multi-channel OTP delivery was implemented to accommodate diverse user preferences and ensure reliable verification across different communication methods. Users could receive verification codes via SMS, WhatsApp, email, or voice calls, with the system automatically selecting the most appropriate channel based on user preferences and delivery success rates. This approach significantly reduced verification failures and improved the overall completion rate of the onboarding process.
The implementation process required careful coordination between multiple stakeholders, including technology teams, compliance officers, and regulatory authorities. The company worked closely with the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) to ensure that the new authentication methods met all regulatory requirements while providing enhanced security compared to traditional approaches. Regular audits and compliance reviews were established to maintain ongoing adherence to evolving regulatory standards.
Training and change management were critical components of the successful implementation. Customer service teams were trained on the new authentication methods to provide support when needed, while compliance teams were educated on the enhanced security features and audit capabilities of the intelligent authentication system. Clear communication with customers about the improved process helped build confidence and trust in the new approach.
The results of the implementation exceeded all expectations. Customer onboarding time was reduced from an average of 3-5 business days to under 10 minutes for the majority of users. The completion rate for new registrations increased from 40% to 92%, representing a significant improvement in customer acquisition efficiency. Customer satisfaction scores for the onboarding process improved dramatically, with users particularly appreciating the speed and convenience of the new system.
From a business perspective, the improved onboarding process enabled the company to scale their customer acquisition efforts significantly. The reduced manual processing requirements allowed compliance teams to focus on higher-value activities, while the improved user experience contributed to increased customer lifetime value and reduced support costs. The company reported a 300% increase in new customer registrations within the first quarter following implementation.
Security metrics also showed substantial improvements. The intelligent authentication system detected and prevented several attempted fraud cases that might have been missed by traditional verification methods. The multi-factor approach and real-time risk assessment capabilities provided stronger protection against identity theft and account takeover attempts. Compliance audits confirmed that the new system exceeded regulatory requirements while providing enhanced security compared to previous methods.
The success of this implementation has broader implications for the Saudi fintech industry and digital transformation initiatives across the Kingdom. It demonstrates that innovative authentication technologies can simultaneously improve user experience, enhance security, and maintain regulatory compliance. The case study provides a blueprint for other financial services companies looking to modernize their customer onboarding processes while meeting the evolving expectations of Saudi consumers.
Looking forward, the company continues to refine and enhance their authentication capabilities. Plans include integration with additional biometric modalities, expansion of risk assessment algorithms, and exploration of emerging technologies like blockchain-based identity verification. The ongoing evolution of the authentication system reflects the company's commitment to maintaining their competitive advantage while providing the best possible experience for their customers.
At Authentica, we've worked with numerous fintech companies across the Middle East to implement similar intelligent authentication solutions. Our platform provides the flexibility and security features necessary to meet diverse regulatory requirements while delivering exceptional user experiences. The success stories from our clients demonstrate the transformative potential of modern authentication technology when properly implemented and integrated with existing business processes.
The future of customer onboarding in the financial services industry will be defined by companies that can successfully balance security, compliance, and user experience. This case study illustrates that with the right technology and implementation approach, it's possible to achieve significant improvements in all three areas simultaneously, creating value for businesses, customers, and regulatory authorities alike.